How Do You Install A Wireless Backup Camera?
How to Install a Wireless Backup Camera: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
With the advent of innovative technology, wireless backup cameras have become an essential accessory for many drivers. These cameras offer improved safety, better visibility, and reduced risks of parking or reversing accidents. They're particularly helpful for large vehicles where standard rear mirrors often fall short. If you’ve recently acquired a wireless backup camera and you’re puzzled about how to install it, you're in the right place. This detailed guide will walk you through the process, step by step, ensuring you install your backup camera with minimum hassle.
Why Choose a Wireless Backup Camera?

Before diving into the steps for installation, it’s useful to understand why wireless backup cameras have gained such popularity. Unlike their wired counterparts, wireless backup cameras eliminate the need to run cables from the back of your vehicle to the dashboard. This makes installation simpler, reduces potential damage, and offers a much cleaner, more convenient solution. Moreover, most wireless backup cameras are compatible with an array of vehicles, from compact cars to RVs.
Now, let’s break the installation process into manageable steps so that even a beginner can effortlessly accomplish the task.
Tools and Materials You'll Need:
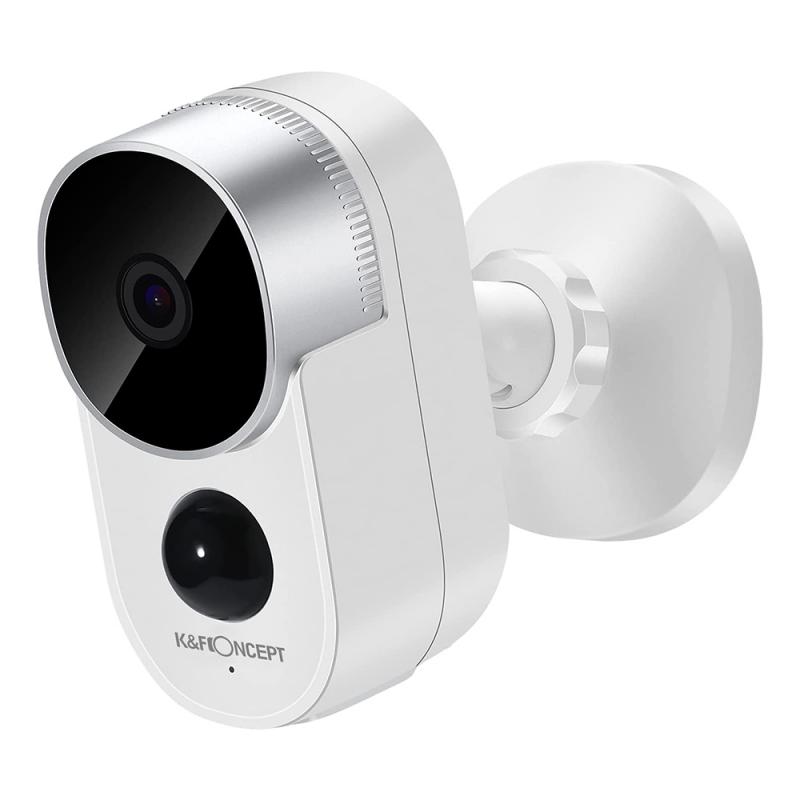

- The wireless backup camera kit
- Screwdriver set (appropriate for your vehicle's screws)
- A power drill (if required for mounting hardware)
- Electrical tape
- Zip ties
- Voltage tester (optional but useful)
- Adhesive pads or mounting brackets (usually included in the kit)
- User manual or instructions included with the backup camera kit
Step 1: Understand Your Wireless Backup Camera Kit

Before beginning the installation, take some time to familiarize yourself with the components in your wireless backup camera kit. A standard kit typically includes:
- The camera unit
- A monitor or display screen
- Transmitter and receiver
- Power wiring
- Necessary mounting hardware
Read through the instruction manual that came with your device to verify that you have all the necessary components and understand how the system works. Additionally, check whether the camera connects with your vehicle’s existing infotainment screen or if it has its own dedicated monitor.
Step 2: Plan the Installation Location
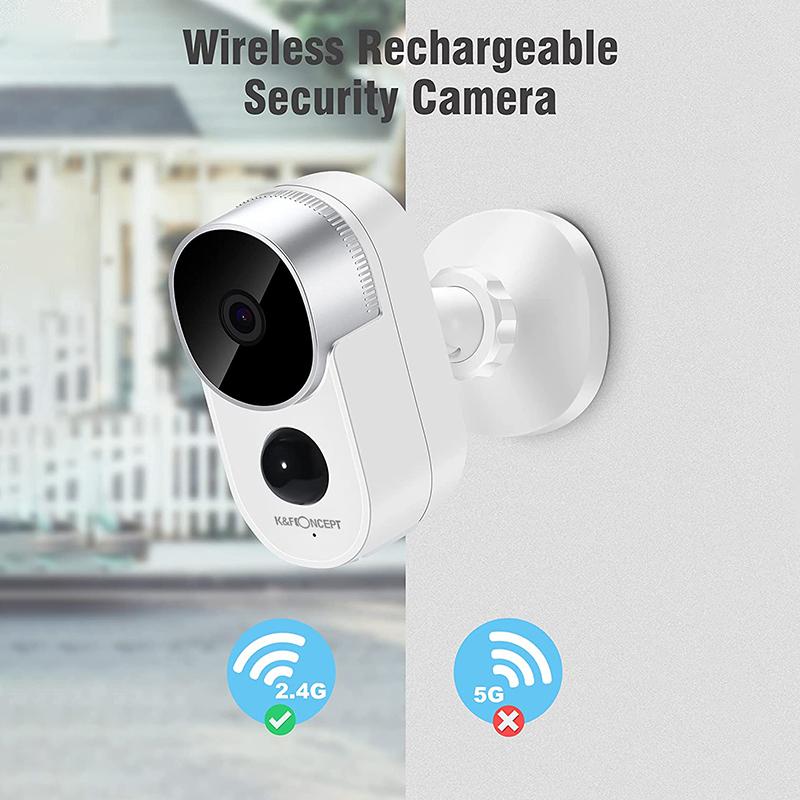

The camera is usually mounted near the back license plate, as this location provides the best rear view. Meanwhile, the monitor or display is installed at the front of the vehicle, often on the dashboard or windshield. It’s advisable to test these positions beforehand so that you’re certain about their practicality and effectiveness.
Step 3: Check the Power Source for Your Camera and Monitor
Wireless backup cameras still require power from your vehicle's electrical system, even though they don’t need to be physically connected to the monitor. There are generally two power options:
1. Camera Power Source:
- Most backup cameras are powered by the reverse light circuit. This means the camera activates automatically when you shift into reverse. To locate the reverse light wiring, open your vehicle’s tail light assembly and use a voltage tester to identify which wire powers the reverse light.
- Use the wiring harness included in your kit to splice into this circuit. Connect the positive wire from the camera to the reverse light's positive wire, and do the same for the negative/ground wire.
2. Monitor Power Source:
- The monitor typically connects to either your car’s cigarette lighter socket or the accessory power outlet. Some systems offer the option to hardwire the monitor into the fuse box if you prefer a cleaner setup.
Step 4: Mount the Camera
After identifying the optimal location for the camera (usually above the rear license plate), attach the mounting bracket provided in the kit. You may need to drill small holes if your vehicle lacks pre-drilled mounting points. Once the bracket is secure:
- Align the camera on the mounting bracket.
- Adjust the angle for the best rear view (you’ll fine-tune this during testing).
- Secure the camera in place using screws or adhesive, depending on the design of your kit.
Step 5: Install the Monitor
Choose a spot for the monitor that is within your line of sight while driving but doesn’t obstruct your view of the road. Common spots include the dashboard, windshield (using a suction cup mount), or a specialized mounting bracket. After setting up the monitor:
- Plug it into its power source (e.g., cigarette lighter or fuse box).
- Position its antenna (if applicable) to maximize wireless signal strength.
Step 6: Establish the Wireless Connection
Wireless backup cameras eliminate the need for running long cables from the back to the front of the vehicle. Once the camera and monitor are powered, they’ll connect automatically via their built-in transmitter and receiver.
Ensure both devices are set to the same frequency (if your kit has adjustable frequencies). You should see the live feed from your camera displayed on the screen. If the connection doesn’t establish automatically:
- Verify that the power connections are secure.
- Confirm that the transmitter and receiver are positioned optimally to reduce interference.
Step 7: Test the System
Before wrapping up the installation, it’s essential to test the functionality of your backup camera system. Shift into reverse gear and check the camera feed on your monitor. Ensure the following:
- The image is clear and not distorted.
- There’s no signal interference or delay.
- The camera angle covers your desired field of vision.
Adjust the camera angle if needed, and confirm that the monitor powers off when you switch out of reverse gear (unless it’s designed to remain on).
Step 8: Secure and Finalize the Setup
Once everything is functioning correctly:
- Use zip ties and electrical tape to neatly secure the wiring.
- Hide or tuck cables into areas where they won’t be exposed or prone to damage.
- Double-check that the installed camera and monitor are stable and won't shift while driving.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with a simple installation process, you might encounter a few hiccups. Here are some troubleshooting tips:
Poor Signal or Interference: Move the transmitter or receiver to reduce obstructions or electrical interference.
Blurry Camera Feed: Clean the camera lens and ensure it is angled correctly.
No Power: Revisit the connection points to make sure all wiring is secure and properly spliced.
Monitor Not Syncing: Check for frequency settings or faulty transmitters/receivers.
Final Thoughts
Installing a wireless backup camera is a straightforward project that most car owners can accomplish with basic tools and a bit of patience. While professional installation is always an option, doing it yourself not only saves money but also provides the satisfaction of learning a new skill. Plus, understanding how your system is set up can be invaluable if troubleshooting is ever required.
The added safety, convenience, and practicality of having a backup camera are well worth the minimal effort of installation. So, follow these steps and enjoy the peace of mind that comes with enhanced rear visibility every time you hit the road. Safe driving!